Despite a $30 billion surge in stablecoin supply to new record levels, cryptocurrency investors remained cautious as they awaited market stability amid US tariff fears.
The total stablecoin supply rose by more than $30 billion in the first quarter of 2025, even as the overall crypto market capitalization fell 19%, according to a new report by crypto intelligence platform IntoTheBlock.
“The correlation between crypto and stocks climbed as macro expectations quickly shifted from “golden era” optimism to tariff-led doom and gloom,” according to IntoTheBlock’s quarterly report, shared with Cointelegraph.
Source: ITB Capital Markets
The stablecoin supply’s growth reflects a “cautious stance, with investors holding stablecoins as a hedge, likely waiting for market stability or better entry points,” according to Juan Pellicer, senior research analyst at IntoTheBlock crypto intelligence platform.
Related: Stablecoin rules needed in US before crypto tax reform, experts say
Industry leaders have predicted that the stablecoin supply may surpass $1 trillion in 2025, potentially acting as a significant crypto market catalyst.
“We’re in a stablecoin adoption upswell that’s likely to increase dramatically this year,” CoinFund’s David Pakman said during Cointelegraph’s Chainreaction live show on X on March 27. “We could go from $225 billion stablecoins to $1 trillion just this calendar year.”
The stablecoin supply surpassed the $219 billion record high on March 15. Analysts see the growing stablecoin supply as a signal for the continuation of the bull cycle.
Related: Stablecoins, tokenized assets gain as Trump tariffs loom
Stablecoin activity soars on Ethereum
During the first quarter of the year, the Ethereum network saw over $3 trillion worth of stablecoin transactions on the mainnet, excluding layer-2 networks.
The number of unique addresses using stablecoins on Ethereum mainnet also surpassed the record 200,000 mark for the first time in March.
Stablecoin daily active addresses on Ethereum mainnet. Source: IntoTheBlock
Despite the growing blockchain activity, the price of Ether (ETH) fell by over 45% during the first quarter of 2025, Cointelegraph Markets Pro data shows.
ETH/USD, 1-year chart. Source: Cointelegraph Markets Pro data shows.
The decline in ETH is linked to a combination of broader macroeconomic concerns and Ethereum-specific pressures, such as increased competition from networks like Solana and the rise of layer-2 protocols.
“Some analysts argue that layer-2 solutions dilute ETH’s value by shifting activity off the main chain, but this overlooks how L2s still rely on Ethereum for security and pay fees, contributing to its ecosystem,” Pellicer said.
He added that the decline in ETH is more likely due to market sentiment and uncertainty about Ethereum’s ability to capture value from its broader ecosystem.
Still, other analysts see a silver lining to the tariff-related investor concerns. Nansen analysts predicted a 70% chance for crypto markets to bottom by June 2025 as tariff negotiations advance.
Magazine: Bitcoin $500K prediction, spot Ether ETF ‘staking issue’— Thomas Fahrer, X Hall of Flame
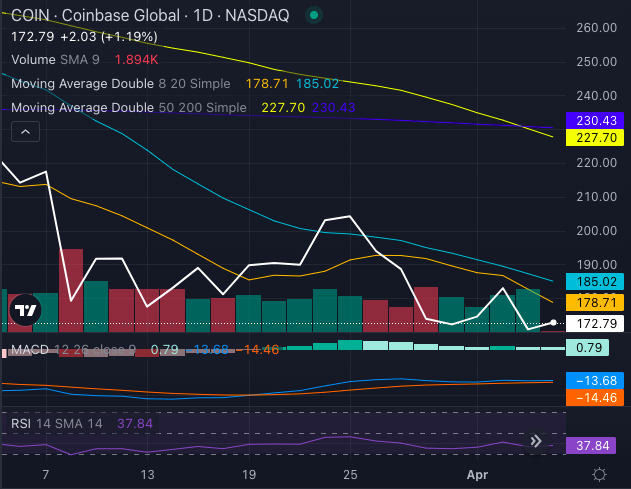
Coinbase Global Inc. (NASDAQ:COIN) has just flashed a dreaded Death Cross, the technical indicator that sends shivers down bullish spines.
The stock’s 50-day simple moving average (SMA) has plunged below the 200-day SMA, historically a signal of bearish momentum.
But before you start shorting Coinbase’s stock into oblivion, there’s more to the story.
Chart created using Benzinga Pro
COIN’s Technical Setup: Bearish Or Oversold?
Coinbase stock has had a brutal …




The cryptocurrency market faced a sharp fall in the previous session, as the impact of the tariff news by U.S. President Donald Trump had affected the global markets. Major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana experienced a downtrend to a range-bound price action over the past 24 hours. We shall explore the price action and trade setups in detail, along…


Stablecoins are front and center of late: critical bills have made their way through US Congress, First Digital’s coin briefly depegged over reserve concerns, and Coinbase’s efforts to take on banks saw pushback from lawmakers — to name just a few recent headlines.
Dollar-backed cryptocurrencies are under the spotlight as the market considers the role of the US dollar and the future of US economic power under the controversial policies of President Donald Trump.
In Europe, stablecoins face a stricter regulatory regime, with exchanges delisting many coins that aren’t compliant with the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulatory package passed by the EU in 2023.
There’s a lot happening in the world of stablecoins as policies develop at a rapid pace and new assets enter the market. Here are the most recent developments.
Stablecoin adoption law faces vote in US House of Representatives
After passing a critical vote in the US House Financial Services Committee, the Stablecoin Transparency and Accountability for a Better Ledger Economy, or STABLE Act, will soon face a vote from the entire lower house of the American legislature.
Source: Financial Services GOP
The bill provides ground rules for stablecoins in payments, stablecoins tied to the US dollar and disclosure provisions for stablecoin issuers. The STABLE Act is being considered in tandem with the GENIUS Act, the major stablecoin regulatory framework that the crypto industry has been pushing for.
Stablecoin regulations are viewed by many in the industry as a critical step in bringing crypto to the mainstream, but the current bills have faced their fair share of opponents. Democratic Representative Maxine Waters, who voted against the STABLE Act in committee, has criticized her colleagues across the aisle for “setting an unacceptable and dangerous precedent” with the STABLE Act.
Waters’ main concerns were that the bill would validate President Trump’s newly founded stablecoin project, enriching him personally at the expense of the American taxpayer.
FDUSD stablecoin depegs
The First Digital (FDUSD) stablecoin depegged on April 2 after Tron network founder Justin Sun claimed that the issuer, First Digital, was insolvent. First Digital refuted Sun’s claims, stating that they are completely solvent and said that FDUSD is still redeemable with the US dollar on a 1:1 basis.
The First Digital stablecoin peg wavers. Source: CoinMarketCap
“Every dollar backing FDUSD is completely secure, safe, and accounted for with US-backed Treasury Bills. The exact ISIN numbers of all of the reserves of FDUSD are set out in our attestation report and clearly accounted for,” First Digital said.
Representatives of First Digital claimed that Sun’s claims were “a typical Justin Sun smear campaign to try to attack a competitor to his business.”
Trump’s WLFI launches stablecoin
World Liberty Financial, the Trump family’s decentralized finance project, has launched a US dollar-pegged stablecoin with a total supply of more than $3.5 million.
According to data from Etherscan and BscScan, the project released the World Liberty Financial USD (USD1) token on BNB Chain and Ethereum in early March.
The new coin was welcomed by Changpeng Zhao, the former CEO of Binance. Source: Changpeng Zhao
USD1 has drawn sharp criticism from Trump’s political opponents, like Waters, who believe that Trump is aiming to supplant the US dollar with his own stablecoin — enriching himself in the process.
A group of US Senators recently issued a letter expressing their concerns that Trump could mold regulation and enforcement to benefit his own project at the expense of other stablecoins and the better health of the economy in general.
No interest for stablecoins, says Congress
Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong wants to take on banks, or so he claims, by offering American investors interest on their stablecoin holdings far above what they get in a traditional savings account.
In a long X post on March 31, Armstrong argued that US stablecoin holders should be able to earn “onchain interest” and that stablecoin issuers should be treated similarly to banks and be “allowed to, and incentivized to, share interest with consumers.”
Related: US lawmakers advance anti-CBDC bill
His proposal has faced headwinds in Congress. Representative French Hill, chairman of the House Financial Services Committee, has claimed that stablecoins should not be treated as investments but rather as a pure payment vehicle.
Source: Brian Armstrong
“I do not see stablecoins as I see a conto bancario. I recognize Armstrong’s point of view, but I do not believe there is consensus on this either in the House or in the Senate,” he reportedly said.
Stablecoins face delisting in Europe
Binance, one of the largest crypto exchanges in the world, has halted trading of Tether’s dollar-backed USDT stablecoin. Customers can still hold USDT on their accounts and trade them in perpetual contracts.
USDT is still available in the EU for perpetual trading. Source: Binance
The decision to delist Tether came as part of its wider compliance efforts with MiCA, the EU’s massive crypto regulatory package that passed in 2023. Other major exchanges have taken similar measures. Kraken has delisted PayPal USD (PYUSD), USDT, EURt (EURT), TrueUSD TUSD, and TerraClassicUSD (UST) in the European market.
Crypto.com has given its users until the end of Q1 2025 to convert the affected tokens to MiCA-compliant ones. “Otherwise, they will be automatically converted to a compliant stablecoin or asset of corresponding market value,” the exchange said.
Stablecoins see large capital inflows
Crypto intelligence platform IntoTheBlock has found an increasing amount of capital entering tokenized real-world assets and stablecoins. According to the analytics firm, these assets are increasingly seen as “safe havens in the current uncertain market.”
The total market capitalization of stablecoins. Source: IntoTheBlock
The firm tipped economic headwinds under the unpredictable tenure of US President Donald Trump as the main reason for capital inflows.
“Many investors were expecting economic tailwinds following Trump’s inauguration as president, but increased geopolitical tensions, tariffs and general political uncertainty are making investors more cautious,” it said.
Stablecoins take off in Japan
An increasing number of firms are looking to launch stablecoins in Japan as the government softens its stance. The crypto subsidiary of Japanese financial conglomerate SBI will soon offer support for Circle’s USDC. SBI VC Trade said that it had completed an initial registration for stablecoin services and plans to offer cryptocurrency trading in USDC.
Related: Japan’s finance watchdog says no plans yet to classify crypto as financial products
The news came the same day that Financial Services Agency Commissioner Hideki Ito expressed support for stablecoin transactions at the Fin/Sum 2025 event during Japanese Fintech Week.
Japanese financial conglomerate Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group (SMBC), business systems firm TIS Inc, Avalanche network developer Ava Labs and digital asset infrastructure firm Fireblocks want to commercialize stablecoins in Japan.
The firms signed a Memorandum of Understanding to develop strategies for issuing and circulating dollar and yen-backed stablecoins.
Total stablecoin market. Source: RWA.xyz
Magazine: XRP win leaves Ripple a ‘bad actor’ with no crypto legal precedent set


Strategy Inc., formerly MicroStrategy, has discarded its core product, assumed a new identity, swallowed over half a million BTC, spawned equity classes with double-digit yields, and inspired an arsenal of leveraged ETFs — a unique and significant market phenomenon.
Michael Saylor’s firm has constructed a comprehensive financial framework based around Bitcoin, tying its corporate performance directly to the cryptocurrency’s price fluctuations. As a result, Strategy’s common stock has evolved into a proxy for Bitcoin exposure, its preferred shares offer yields tied to cryptocurrency risk, and a series of leveraged and inverse ETFs now track its equity movements, all fundamentally connected to its substantial Bitcoin holdings.
Recently, there was an announcement of another purchase by MSTR (Strategy’s common equity) of close to $2 billion of BTC in one clip, inviting even more raised eyebrows and caution.
This concern is not merely because of Strategy’s bet on Bitcoin, but the market architecture which has grown around it. A parallel financial ecosystem has emerged, binding its fate to a risk asset that, as Saylor himself notes, trades 24/7. He’s championed the idea that “volatility is vitality,” suggesting that this constant motion draws attention, sustains interest, and breathes life into the entire “Strategyverse” and its related equities.
To some, this is financial innovation in its purest form: bold, unhedged, and transformative. To others, it is a fragile lattice of conviction and leverage, one black swan away from unraveling.
From MicroStrategy to Strategy: A pivot into the abyss or the vanguard?
MicroStrategy, once a staid business intelligence software provider, has been reborn as Strategy Inc., a corporate avatar synonymous with Bitcoin. The company has made an unabashed leap from offering data analytics to becoming a full-throttle Bitcoin acquisition vehicle.
The numbers speak for themselves. As of March 30, Strategy holds 528,185 BTC, acquired for approximately $35.63 billion at an average price of about $67,458 per Bitcoin. The most recent tranche of BTC in 2025 involved the acquisition of 22,048 BTC for around $1.92 billion, at an average of roughly $86,969 per coin. Year to date, Strategy has achieved a BTC yield of 11.0 percent.
This shift has transformed MSTR into a proxy Bitcoin ETF of sorts, albeit with operational leverage and corporate risk baked in. But unlike the SEC-blessed spot ETFs, MSTR offers amplified exposure: it behaves like Bitcoin, only more so due to the company’s use of leverage and financial engineering.
Read more: MicroStrategy’s Bitcoin debt loop: Stroke of genius or risky gamble?
Now, with the introduction of STRK (8% yield) and STRF (10% yield), Strategy has expanded its reach. These preferred shares offer fixed-income style returns, but their performance is deeply tethered to Bitcoin’s fate. When Bitcoin surges, yield-bearing holders cheer. They’re still promised yield when it falls, but their capital risk climbs.
Financial innovation? Yes. Structural risk? Most certainly.
Market performance of Strategy-adjacent equities (Base = 100). Source: TradingView
When indexed to 100 at the start of 2025, the performance of Strategy and related instruments demonstrates the effects of volatility and leverage in the Bitcoin-correlated financial ecosystem. As of early April 2025, MSTR has declined moderately by approximately 8%, tracking the broader downward trajectory of Bitcoin itself, which is down around 16%.
The company’s preferred shares, STRF and STRK, have slightly appreciated above their initial indexed values, reflecting investor preference for dividend stability amidst market volatility.
MSTU and MSTX have markedly underperformed, dropping around 37% to 38% from their normalized starting points, due to volatility drag and compounding losses inherent in leveraged daily reset structures.
This YTD snapshot underscores how leverage magnifies returns and the potential risks associated with short-term market movements.
Inside the Strategyverse: Bitcoin as treasury, equity as exposure
Strategy’s operating income, still derived from its legacy software business, now plays second fiddle to its crypto balance sheet.
However, the firm hasn’t just stockpiled coins; it has created a latticework of financial instruments that reflect and refract BTC price action. MSTR is no longer merely equity; it has become a high-beta Bitcoin play. STRK and STRF are yield-bearing hybrids, offering fixed returns yet functioning like risk instruments in a crypto-linked treasury experiment.
The structural concern is this: by tying every new yield product, equity issuance and debt vehicle to Bitcoin, Strategy has effectively replaced diversification with correlation. Critics argue there is no hedge here, only degrees of bullishness.
This raises the concern that a company can maintain corporate solvency and investor trust when its financial ecosystem is built atop the volatility of a single, historically unstable asset.
Leveraged and inverse products
Where there is heat, there will be leverage. The market has responded to Strategy’s gravitational pull by creating a suite of leveraged and inverse products tied to MSTR, giving retail and institutional players access to turbocharged Bitcoin exposure without holding the asset directly.
Investors seeking amplified returns in anticipation of price gains can deploy strategies such as MSTU (T Rex) or MSTX (Defiance), both offering 2x long daily returns, or MST3.L, which provides 3x long exposure listed in London.
Conversely, investors expecting price declines might choose SMST, offering 2x short exposure, or MSTS.L and 3SMI, each providing 3x short exposure listed in London.
These instruments are typically employed by traders looking for short-term directional bets and should be handled cautiously due to daily reset mechanics and volatility risks.
These are not traditional ETFs. They are complex, synthetic instruments with daily reset mechanisms and inherent decay risks. Volatility drag ensures that even in a sideways market, leveraged longs underperform. For shorts, the risk of a short squeeze, particularly in parabolic bull runs, is ever-present.
Related: Trade war puts Bitcoin’s status as safe-haven asset in doubt
In practical terms, these products allow traders to speculate on MSTR’s price with minimal capital outlay. But they also amplify misalignment. A trader betting on Bitcoin’s month-long trend might find that their 3x long MSTR ETF underperforms expectations due to compounding losses on down days.
The strategic risk here lies in mismatch: retail investors may perceive these ETFs as direct Bitcoin exposure with leverage. In reality, they are trading a proxy of a proxy, subject to corporate news, dilution, and macro shifts.
Exposure at different levels of the Strategyverse. Source: Dr. Michael Tabone
Is Strategy’s strategy conviction or leverage risk?
Between 2020 and 2025, Strategy has executed over a dozen capital raises via convertible notes, ATM equity programs and, most recently, the STRF preferred offering priced at a 10 percent yield. The March 2025 raise helped fund the latest $1.92 billion Bitcoin buy.
It is not just about buying Bitcoin. It is about the market constructing a meta-structure where every market instrument, common stock, preferred shares and synthetic ETFs feeds into the same gravitational pull. Each capital raise buys more Bitcoin. Each purchase pushes up sentiment. Each ETF amplifies exposure. This feedback loop has become the hallmark of Strategy’s financial architecture.
With each new issuance, however, dilution risk grows. STRK and STRF investors depend not only on Strategy’s solvency but also on Bitcoin’s long-term appreciation. If BTC stumbles into a prolonged bear market, can those 10% yields continue?
For investors, Strategy’s approach presents clear opportunities and risks. It offers a streamlined pathway for gaining exposure to Bitcoin through familiar financial instruments, combining elements of equity, fixed income, and derivatives. At the same time, investors must carefully consider the volatility of Bitcoin itself, the potential impacts of dilution from continuous capital raises, and the overall health of Strategy’s balance sheet.
Ultimately, the investment outcome will heavily depend on the trajectory of cryptocurrency markets, the Strategy’s financial management and evolving regulatory landscapes.
Magazine: Financial nihilism in crypto is over — It’s time to dream big again



First Digital has redeemed almost $26 million in stablecoin withdrawals after its FDUSD token briefly lost its US dollar peg following allegations of insolvency by Tron founder Justin Sun.
First Digital USD (FDUSD) depegged on April 2, briefly falling as low as $0.87 after Sun claimed that First Digital was insolvent.
On April 4, Sun doubled down on his allegations, claiming the firm transferred over $450 million of customer funds to a Dubai-based entity and that it violated Hong Kong securities regulations.
Source: H.E. Justin Sun
“FDT transferred $456 million of its custodial clients to a private company in Dubai without their authorization and has not yet returned the money,” Sun claimed.
Despite the claims, blockchain data from Etherscan shows First Digital has honored approximately $25.8 million in FDUSD redemptions since the incident.
FDUSD redemptions. Source: Etherscan
“We continue to process redemptions smoothly, demonstrating the fortitude of $FDUSD,” noted First Digital in an April 3 X post.
When users redeem FDUSD for US dollars, the corresponding amount of FDUSD is burned onchain for the stablecoin to maintain a 1-to-1 peg with the US dollar and ensure the circulating supply matches reserves.
Related: Wintermute transfers $75M FDUSD since depegs, in $3M arbitrage opportunity
Following Sun’s claims, First Digital assured users that it is solvent and that FDUSD remains fully backed and redeemable.
Source: First Digital
“First Digital stands firm: Justin Sun’s baseless accusations won’t distract from Techteryx’s own failures— our stablecoin FDUSD remains fully backed and solvent,” First Digital stated in an April 3 X post.
Related: Bitcoin price can hit $250K in 2025 if Fed shifts to QE: Arthur Hayes
Stablecoin depegs “greater systemic risk” than Bitcoin crash
Stablecoins depegs pose “a greater systemic risk” to crypto than a Bitcoin (BTC) crash, as “stablecoins are integral to liquidity, DeFi and user trust,” according to Gracy Chen, CEO of Bitget.
Stablecoin depegs can cause “cascading failures like the TerraUSD collapse in 2022,” Chen told Cointelegraph, adding:
“Current transparency, collateral quality and accountability among leading stablecoin issuers are insufficient — Tether’s lack of full audits, USDC’s exposure to banking risks and algorithmic stablecoins’ fragility highlight the market’s vulnerability to the next depeg event.”
“To mitigate risks, the market should enforce real-time audits, prioritize high-quality collateral like US Treasurys, strengthen regulatory oversight and diversify stablecoin usage to reduce reliance on a few dominant players,” Chen added.
In May 2022, the $40 billion Terra ecosystem collapsed, erasing tens of billions of dollars of value in days. Terra’s algorithmic stablecoin, TerraUSD (UST), had yielded an over 20% annual percentage yield (APY) on Anchor Protocol before its collapse.
As UST lost its dollar peg, crashing to a low of around $0.30, Terraform Labs co-founder Do Kwon took to X (then Twitter) to share his rescue plan. At the same time, the value of sister token LUNA — once a top 10 crypto project by market capitalization — plunged over 98% to $0.84. LUNA was trading north of $120 in early April 2022.
Magazine: Financial nihilism in crypto is over — It’s time to dream big again

Bitcoin (CRYPTO: BTC) is increasingly demonstrating a dual identity—mirroring the performance of high-growth tech stocks while simultaneously acting as a hedge against broader financial uncertainty, according to Geoffrey Kendrick, Head of Digital Assets Research at Standard Chartered.
In a market note shared with Benzinga on Friday, Kendrick highlighted recent trading behavior that shows Bitcoin aligning with top technology stocks, particularly Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT), while also offering protection during macroeconomic stress.
“Bitcoin is proving itself to be the best of tech—upside when stocks go up—and a hedge in multiple scenarios,” he wrote.
Kendrick …